Loop nesting refers to the practice of placing one or more loops inside another loop. This is done to create more complex looping patterns and to solve problems that require multiple levels of iteration.
Example 1) Loop nesting with an outer loop running
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
// Example of a simple for loop
printf("Example of a simple for loop:\n");
for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {
printf("%d ", i);
}
printf("\n");
// Example of loop nesting
printf("\nExample of loop nesting:\n");
for (int outer = 1; outer <= 3; outer++) {
printf("Outer Loop Iteration %d:\n", outer);
for (int inner = 1; inner <= 2; inner++) {
printf(" Inner Loop Iteration %d\n", inner);
}
}
return 0;
}
- The first part of the code demonstrates a simple
forloop that prints numbers from 1 to 5. - The second part illustrates loop nesting, where an outer loop runs three times, and for each iteration of the outer loop, an inner loop runs twice. This results in a total of 3 (outer) * 2 (inner) = 6 iterations.
Output
Example of a simple for loop:
1 2 3 4 5
Example of loop nesting:
Outer Loop Iteration 1:
Inner Loop Iteration 1
Inner Loop Iteration 2
Outer Loop Iteration 2:
Inner Loop Iteration 1
Inner Loop Iteration 2
Outer Loop Iteration 3:
Inner Loop Iteration 1
Inner Loop Iteration 2
This output demonstrates the execution of both a simple for loop and loop nesting in a C program.
Nesting loops can occur an infinite number of times. When programming, remember to align each loop properly, making it easy to read and understand.
Do it for yourself and for others. Sometimes, when you revisit a program you wrote after some time, it might not be very clear.
Nesting loops are often used in array and matrix operations.
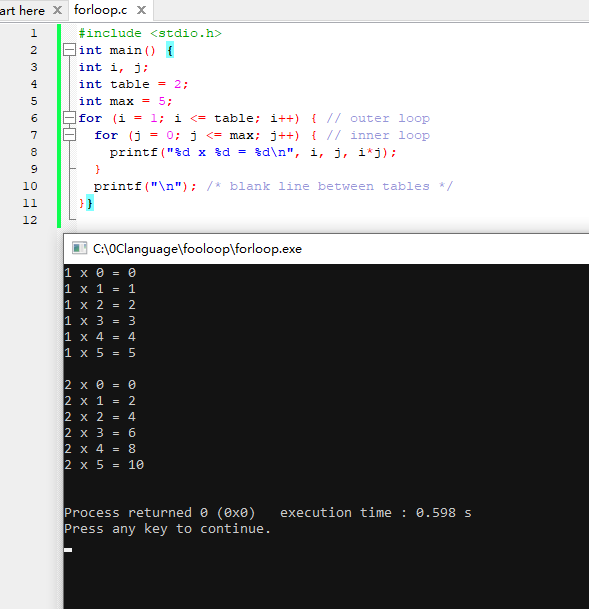
Example 2) The nested for loop statement outputs a multiplication table.
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int i, j;
int table = 2;
int max = 5;
for (i = 1; i <= table; i++)
{ // outer loop
for (j = 0; j <= max; j++)
{ // inner loop
printf("%d x %d = %d\n", i, j, i*j);
}
printf("\n"); /* blank line between tables */
}
}
Output