1. Load Store Instructions
RV32I is a load-store architecture. Only load and store instructions can access memory and peripherals (registers inside the CPU can only be operated by arithmetic instructions).
Load and store instructions exchange values between registers and memory/peripherals.
The load instruction is encoded as I-type with an opcode of 0000 011, while the store instruction is encoded as S-type with an opcode of 0100 011, as shown in Figure 1.
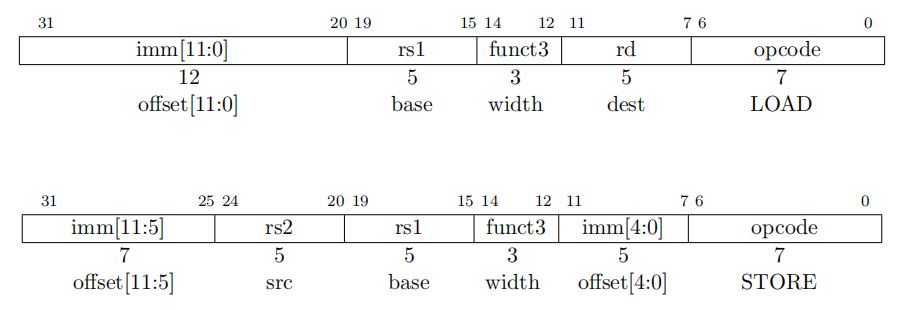
The effective address is obtained by adding the sign-extended 12-bit immediate value (in the case of the store instruction, the immediate value is split into two parts) to the value in the rs1 register.
Generally, the load instruction copies the value at the effective address in memory/peripherals to the rd register, while the store instruction copies the value in the rs2 register to the effective address in memory/peripherals.
2. LOAD
2.1.LW
Load Word
Instruction Format:
LW rd,offset(rs1). x[rd] = sext ( M [x[rs1] + sext(offset) ] [31:0] )

As Shown in Figure 2.
- opcode:000 0011
- funct3: 010
This instruction reads four bytes (one word) from the effective address and writes it into the rd register.
2.1.1 Example
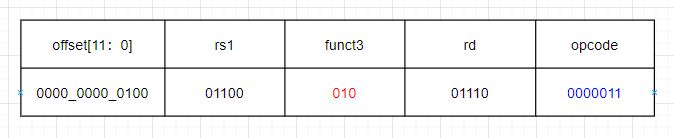
LW x13,4(x12)
Read four bytes from the memory address corresponding to the value in register x12 plus a 4-byte offset, and store the result in register x13.
- opcode: 000_0011
- funct3: 010
- immediate: 12’b0000_0000_0100
- rs1: 5’b0_1100
- rd: 5’b0_1101
the machine code for LW x13, 4(x12) is 0000 0000 0100 0110 0010 0110 1000 0011Hex: 32’h0046_2683
2.2.LH
Load Halfword
Instruction Format:
LH rd,offset(rs1). x[rd] = sext( M [x[rs1] + sext(offset)] [15:0])

As Shown in Figure 3.
- opcode:000 0011
- funct3: 001
This instruction reads two bytes (halfword) from the effective address, sign-extends it, and writes the result into the rd register.
2.2.1 Example
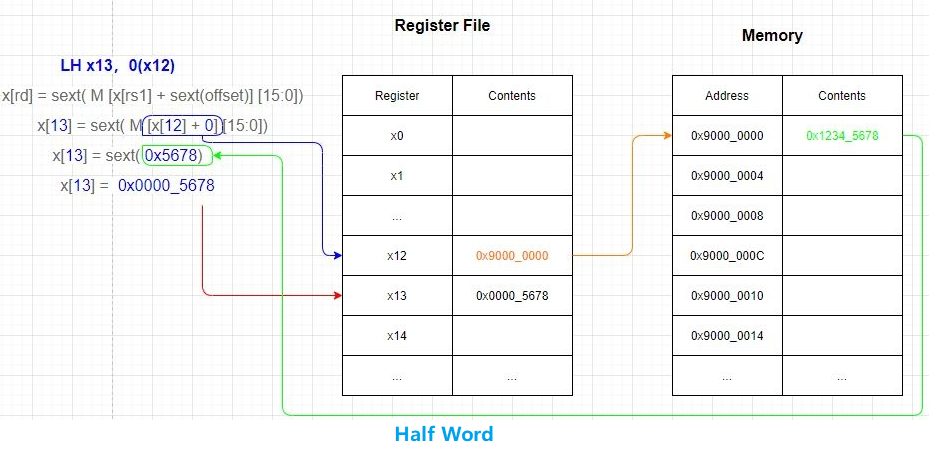
LH x13,0(x12)
Read two bytes from the memory address corresponding to the value in register x12, sign-extend it, and store the result in register x13, as shown in the following figure
2.3.LHU
Load Halfword,Unsigned
Instruction Format:
LHU rd,offset(rs1). x[rd] = M[x[rs1] + sext(offset)][15:0]

As Shown in Figure 5.
- opcode:000 0011
- funct3: 101
This instruction reads two bytes (halfword) from the effective address, zero-extends it, and writes the result into the rd register.
2.3.1 Example
LHU x13,0(x12)
Read two bytes from the memory address corresponding to the value in register x12, zero-extend it, and store the result in register x13.
2.4.LB
Load Byte
Instruction Format:
LB rd,offset(rs1). x[rd] = sext( M [x[rs1] + sext(offset)] [7:0])

As Shown in Figure 6.
- opcode:000 0011
- funct3: 000
This instruction reads a byte from an effective address, sign-extends it, and then writes it into the rd register.
2.4.1 Example
LB x13,0(x12)
Read a byte from the corresponding address in the x12 register, sign-extend it, and store it in the x13 register.
2.5. LBU
Load Byte,Unsigned
Instruction Format:
LBU rd,offset(rs1). x[rd] = M[x[rs1] + sext(offset)][7:0]

As Shown in Figure 7.
- opcode:000 0011
- funct3: 100
This instruction reads a byte from an effective address, zero-extends it, and then writes it into the rd register.
2.5.1 Example
LBU x13,0(x12)
Read a byte from the corresponding address in the x12 register, zero-extend it, and store it in the x13 register.
3. STORE Instructions
3.1 SW
Store Word
Instruction Format:
SW rs2,offset(rs1)。M[x[rs1] + sext(offset)]= x[rs2][31: 0]

As Shown in Figure 8.
- opcode:010 0011
- funct3: 010
This instruction stores a word, which is four bytes, from the rs2 register into the effective address.
3.1.1 Example
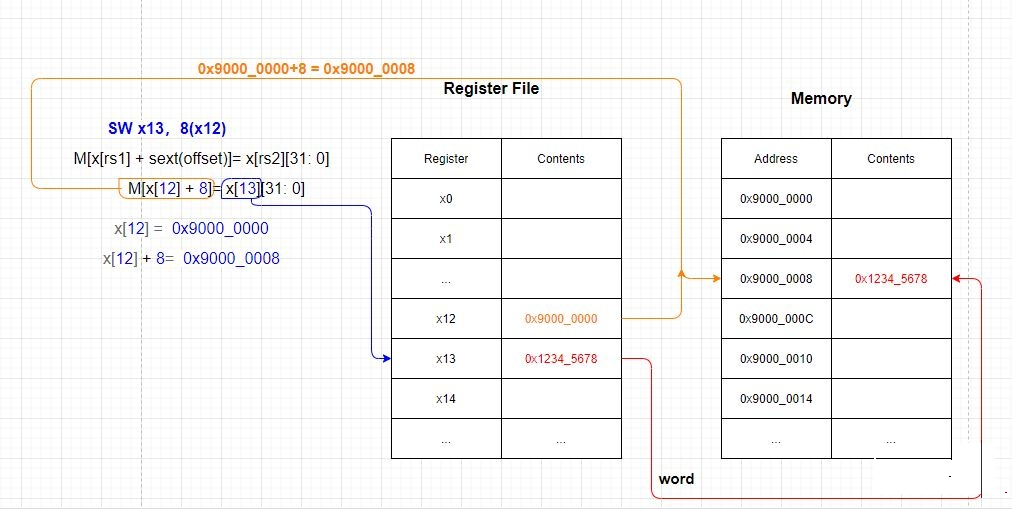
SW x13,8(x12)
Store the four bytes from the x13 register into the effective address computed by adding the value in the x12 register with an offset of 8.
3.2 SH
Store Halfword
Instruction Format:
SH rs2,offset(rs1). M[x[rs1] + sext(offset)] = x[rs2][15: 0]

As Shown in Figure 10.
- opcode:010 0011
- funct3: 001
This instruction stores a halfword, which is two bytes, from the rs2 register into the effective address.
3.2.1 Example
SH x13,0(x12)
Store the low-order two bytes from the x13 register into the corresponding address in the x12 register.
3.3 SB
Store Byte
Instruction Format:
SB rs2,offset(rs1). M[x[rs1] + sext(offset)]= x[rs2][7: 0]

As Shown in Figure 11.
- opcode:010 0011
- funct3: 000
This instruction stores the low-order byte (i.e., the least significant byte) from the rs2 register into the effective address.
3.3.1 Example
SB x13,0(x12)
Store the low-order byte (i.e., the least significant byte) from the x13 register into the corresponding address in the x12 register.